Hair loss is a natural part of life and can occur for various reasons, sometimes leading to permanent bald patches. However, if you're experiencing lasting hair loss, it can be effectively treated with a hair transplant.
This surgical procedure involves relocating hair follicles from a donor area-commonly the back or sides of the scalp, but also potentially from the beard, chest, abdominal, pubic, or lower limb areas-to a bald or thinning part of the scalp, known as the recipient area.
The most critical factor in hair transplantation for male pattern baldness (MPB) patients is the efficient implementation of the donor-recipient ratio. However, there is no known element that scientifically predicts the standard of progression of alopecia or indicates a permanently safe donor area.
While the increasing popularity for hair transplants pieces of advice that more people are successfully regaining their hairline and curing baldness, the reality is that in order to be a good candidate for the procedure there is more cardinal than just being bald.
This procedure is primarily used to treat male pattern baldness but can also be applied to restore eyelashes, eyebrows, beard hair, and chest hair.
The most important factors in hair transplantation of male pattern baldness (MPB) are the management of the donor area, precise assessment, the designing and planning of the recipient area by taking long-term progress into consideration. A safe donor area is expected to be permanently covered with hair for a lifetime and therefore, provide permanent coverage when transplanted to the recipient area. We provide you with some better indication on what makes a good candidate or not, the key elements that may affect your candidacy:
The most important factors in hair transplantation of male pattern baldness (MPB) are the management of the donor area, precise assessment, the designing and planning of the recipient area by taking long-term progress into consideration. A safe donor area is expected to be permanently covered with hair for a lifetime and therefore, provide permanent coverage when transplanted to the recipient area. We provide you with some better indication on what makes a good candidate or not, the key elements that may affect your candidacy:
While there isn't an age limit on who can experience a hair transplant procedure, it still plays a role and admirably the best candidates are over 20 to 23 years old. Some candidates can begin losing their hair at a very young age and hope to seek out the treatments as soon as possible.
However, younger patients in their late teens, early twenties are still experiencing immature hair loss and there are no assumptions how this will progress with age. If they are proceeding for Hair transplant in young age, they may need additional surgery later in life to treat further baldness.
The severity of hair loss in patients, as well as the availability of donor's hair, will play a critical role in whether they will make a good candidate, necessarily, in order to be able to transfer hair from one area of the scalp to the affected areas; there must be a good available supply of healthy hair follicles. Assessing the level of hair loss, quality and quantity of donor's hair is an essential part to understand if you're a good candidate or not.
As hair transplants are a surgical treatment, in order to be a good candidate you must be having good general health. Eating a healthy diet, taking regular exercise, looking after yourself and making good lifestyle choices will all work to boosting your immune system.
This will help to improve recovery time period from a hair transplant as your body will provide better to heal more quickly. If you suffer from any other long-term health issues you should make sure your surgeon about them.
The candidates for hair transplants are those who suffer from male or female pattern baldness. This is a genetic circumstance that typically affects the parts of scalp not on all the area, which can be leaves patients with a good level of donor hair follicles. On the other side, un-patterned alopecia sufferers would not be recommended hair transplants as they can be treated with nonsurgical medical treatments like PRP and food supplements.
The types of hair you have can make a difference. Although it is possible to do hair transplants on all types of hair, if you have thicker hair more coverage it will give in bald spots area and similarly hair that's curly or wavy will also give an appropriate coverage in affected areas.
Of course, every case varies from other, so if you want to find out if you would be a good candidate for successful hair transplants the best thing to do is seek professional advice at the hair transplant clinic.
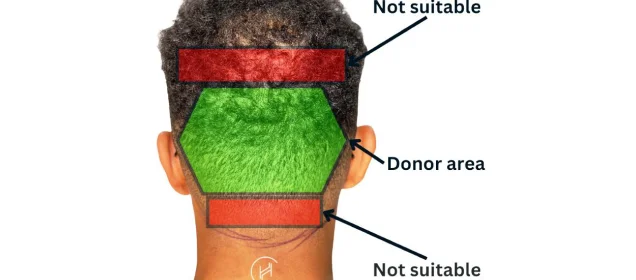
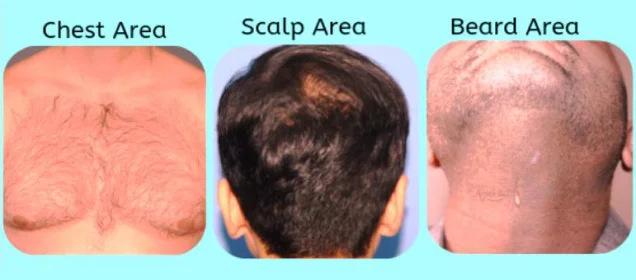
Male pattern baldness and female pattern baldness both are the terms used to represent Androgenic Alopecia. That is because, there is a pattern to the baldness. Especially in men, no matter how much hair they have lost in the top, front and crown areas of their heads, the backs and sides of their heads retain hair; sometimes it happens more than this.
The back and sides are far less affected by the action of DHT (Di hydro testosterone) on their hair follicles. These areas are the donor hair sites. With the availability of the body hair as a donor source (beard, chest, and abdomen) advanced grade of baldness can also get a head full of hair after hair transplant surgery.
In Norwood grade IV to VII we can use scalp hair as a donor along with the combination of the body hair to increase the number of grafts to be implanted, depending on the patient's expectation and requirement.
Also known as strip harvesting. Involves removing a strip of scalp from the donor area, which is then dissected into individual follicular units and transplanted to the recipient area.Leaves a linear scar in the donor area, which can be concealed by surrounding hair.
Involves harvesting individual hair follicles directly from the donor area. Minimally invasive with tiny, dot-like scars. Allows for a quicker recovery compared to FUT.
The process begins with a consultation with a hair transplant surgeon to assess the extent of hair loss, determine candidacy, and plan the procedure. The surgeon will design the hairline and identify the donor and recipient areas.
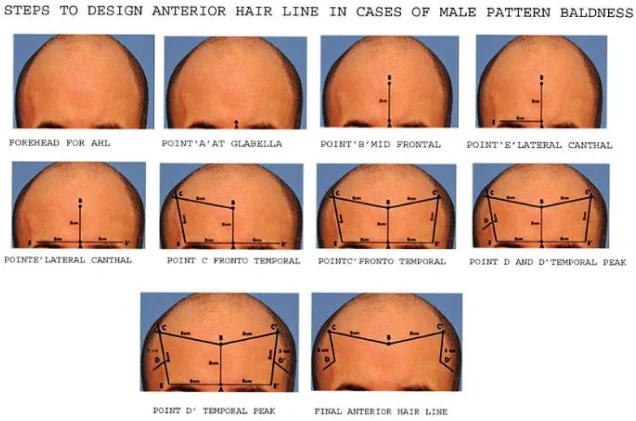
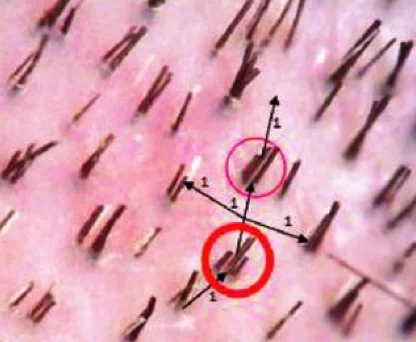
The surgeon makes tiny incisions in the recipient area (Slit making). Hair follicles are carefully placed into these incisions, ensuring the correct angle and direction to achieve a natural appearance.
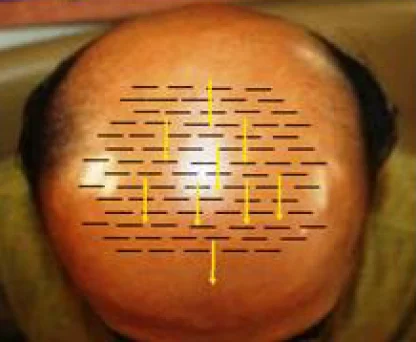

| Recipient Site | Angle of Slit | Follicular Units Density | Pattern |
|---|---|---|---|
| Frontal Hairline | Acute < 45° | 20-30 grafts/cm2 | Irregularly Irregular |
| Temporal Areas | Acute < 45° | 30-35 grafts/cm2 | Radial pattern extending outwards or patient's natural pattern of hair-angles |
| Vertex | 45° | 40-45 grafts/cm2 | Whorled Pattern |

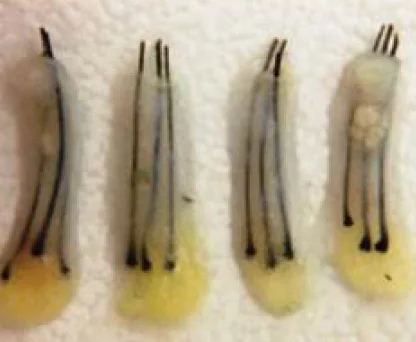
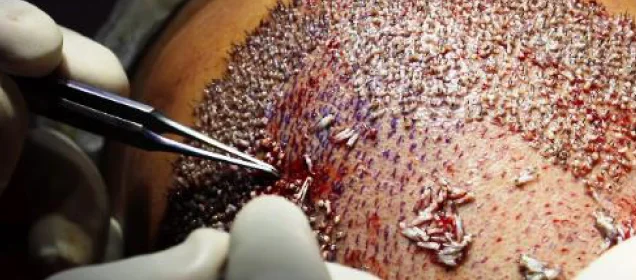
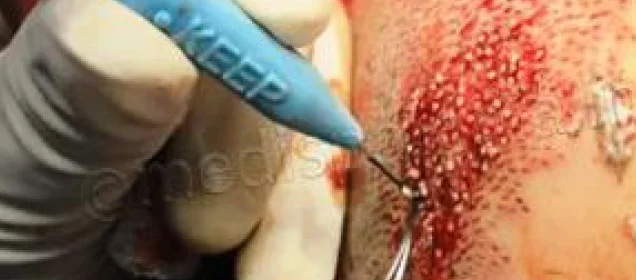
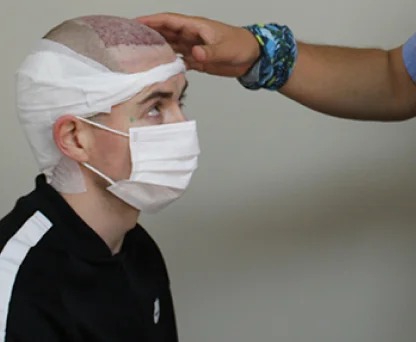
After the procedure, the scalp may be tender, and patients may need pain medications. The transplanted hair will fall out within a few weeks, but new growth should begin within a few months.
Full recovery from a hair transplant procedure usually takes a few months. New hair growth typically becomes noticeable after three to four months, with full results visible after about a year. Patients may need to follow specific aftercare instructions, including avoiding of strenuous activities, exposure to direct sunlight and to continue year long anti hair fall medications.
The cost of a hair transplant varies widely depending on the extent of hair loss, the type of procedure, the surgeon's expertise, and the geographical location. It is generally not covered by insurance companies as it is considered a cosmetic procedure.
Hair transplants can significantly improve the appearance and self-esteem of individuals experiencing hair loss. Advances in techniques, particularly the development of FUE, have made the procedure less invasive and more natural-looking. However, careful consideration and consultation with a qualified surgeon are crucial for achieving the best possible outcome.