
Acne is a common skin condition that happens when hair follicles under the skin become clogged. Sebum-oil that helps keep skin from drying out-and dead skin cells plug the pores, which leads to outbreaks of lesions, commonly called pimples or zits. Most often, the outbreaks occur on the face but can also appear on the back, chest and shoulders.
People of all races and ages get acne, but it is most common in teens and young adults. When acne appears during the teenage years, it is more common in males. Acne can continue into adulthood, and when it does, it is more common in women.
Acne causes several types of lesions, or pimples. Doctors refer to enlarged or plugged hair follicles as comedones. Types of acne include :
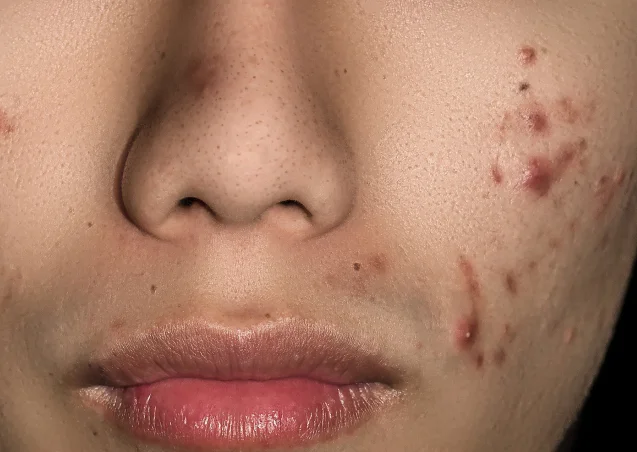
Acne causes several types of lesions, or pimples. Doctors refer to enlarged or plugged hair follicles as comedones. Types of acne include :
Acne is due to a combination of factors such as :
The following factors may increase your risk for developing acne:
Hormones : An increase in androgens, which are male sex hormones, may lead to acne. These increase in both boys and girls normally during puberty and cause the sebaceous glands to enlarge and make more sebum. Hormonal changes related to pregnancy can also cause acne.
Acne is due to a combination of factors such as :
The following factors may increase your risk for developing acne:
Hormones : An increase in androgens, which are male sex hormones, may lead to acne. These increase in both boys and girls normally during puberty and cause the sebaceous glands to enlarge and make more sebum. Hormonal changes related to pregnancy can also cause acne.
Family History : You may be more likely to get acne if your parents had acne.
Medications : Certain medications, such as medications that contain hormones, corticosteroids, and lithium, can cause acne.
Age : People of all ages can get acne, but it is more common in teens.
Flares of acne can be provoked by :
To diagnose acne, doctors may :
In most cases, tests are unnecessary. If features are atypical consider :
The goals of treatment are to help heal existing lesions, stop new lesions from forming, and prevent scarring. Medications can help stop some of the causes of acne from developing, such as abnormal clumping of cells in the follicles, high sebum levels, bacteria, and inflammation. Your doctor may recommend over-the-counter or prescription medications to take by mouth or apply to the skin.
Topical medications, which you apply to the skin, include :
For some people, the doctor may prescribe oral medications, such as:
Some people who have severe acne or acne scarring that does not respond to topical or oral medications may need additional treatments, such as :
If you have acne, the following recommendations may help you in taking care of your skin.